The reason of our thus treating composts of various soils and substances, is not only to dulcify, sweeten, and free them from the noxious qualities they otherwise retain. ... [Before composting, they are] apter to ingender vermin, weeds, and fungous ... than to produce wholsome [sic] plants, fruits and roots, fit for the table.
—J. Evelyn, 17th century
Decomposition of organic materials takes place naturally in forests and fields all around us. Composting is the art and science of combining available organic wastes so that they decompose to form a uniform and stable finished product. Composts are excellent organic amendments for soils. Composting reduces bulkiness of organic materials, stabilizes soluble nutrients and hastens the formation of humus. Most organic materials can be composted, and the process offers a win-win opportunity: reducing waste and improving soil.
In some ways, composting is microbe farming. If ingredients are combined to provide food (carbon and nitrogen), moisture, oxygen and shelter in proper proportions, a diverse cohort of organisms will efficiently process the feedstock. These microorganisms perform well at elevated temperatures with plenty of oxygen and moisture. They cover the range of warm (mesophilic) to hot (thermophilic) conditions. Thermophilic temperatures (from 110° up to 160°F) help kill off weed seeds and disease organisms, which sets composting apart from other decomposition processes. At temperatures below 110°F, the more prolific mesophilic organisms take over and the rate of composting again slows down, especially as it drops toward ambient temperatures, a process known as “curing.” At the other extreme, temperatures above 160°F can develop in compost piles; this overheating slows down the composting process by killing off most organisms and by possibly causing extreme drying. High temperatures, in combination with high ambient temperatures and aeration, can also cause spontaneous combustion in barns and at compost facilities. In general, the composting process is slowed by anything that inhibits good aeration or the maintenance of high enough temperatures and sufficient moisture. It has been found that mesophilic temperatures may be more effective at breaking down some pharmaceuticals.
TYPES OF COMPOSTING
Some people talk about “low temperature” composting—including “sheet,” worm (vermicomposting) and small-pile composting—and “high temperature” composting. We like to use the term “composting” only when talking about the rapid decomposition that takes place at high temperatures.
EVEN BIRDS DO IT
The male brush turkey of Australia gathers leaves, small branches, moss and other litter and builds a mound about 3 feet high and 5 feet across. It then digs holes into the mound repeatedly and refills them, helping to fragment and mix the debris. Finally, the pile is covered with a layer of sticks and twigs. The female lays her eggs in a hole dug into the pile, which heats to nearly 100°F around the eggs, while the outside can be around 65°F. The heat of the composting process frees the birds from having to sit on the eggs to incubate them.
—R.S. Seymour (1991)
Making Composts
A SAMPLE RECIPE FOR BACKYARD COMPOSTING
Start with the following:
- grass clippings (77% moisture, 45% C and 2.4% N)
- leaves (35% moisture, 50% C and 0.75% N)
- food scraps (80% moisture, 42% C and 5% N)
The ratio of the materials needed to get 60% moisture and a C:N of 30:1 is 100 pounds of grass, 130 pounds of leaves and 80 pounds of food scraps.
—T. Richard (1996b)
Common and Uncommon Feedstock
Composting of wastes and organic residues, both on and off farms, has become a more common practice. Farmers, municipalities and community composters accept many organic residuals, and tipping fees are often charged to offset the cost of managing this waste.
The list of source materials is endless and includes anything, plant or animal, that was alive and is now dead and needs to be managed. Some examples include crop residuals; food processing residuals; livestock carcasses; pet, zoo and human manure; chipped trees; mixed leaf and yard residuals; road kill; egg shells; glucose solutions; brewery waste; paper from document destruction; bakery excess; floral and cut flower production waste; coffee/tea grounds; off-spec human food; residuals from fish canneries and slaughterhouses; poultry feathers; livestock wool; butcher waste; fish from fish kills; aquatic weeds; biochar; whey and other milk products; fats/oils/greases; bagasse (the pulpy residue left from crushing and extracting liquid from sugar cane); drywall; and untreated small pieces of wood.
Feedstock materials cannot just be thrown together randomly; they require a recipe that allows for the appropriate physical conditions (e.g., allowing air flow and the right texture for handling) and lots of carbon and nitrogen available for the microorganisms to feed on. Compost piles are often built by alternating layers of these materials. Turning the pile mixes the materials. Composting occurs most easily if high-nitrogen materials are mixed with high-carbon materials, with the average C:N ratio of the materials being about 25–40 parts carbon for every part nitrogen (see Chapter 9 for a discussion of C:N ratios). Therefore, manure mixed with straw, wood chips or bark can be composted as is, because it has the right C:N balance. Wood chips or bark also provide the coarse structural matrix (skeleton) needed for airflow and handling, and may be recycled by shaking the finished compost out of the bulking material and then used for the next composting cycle. Manure and sawdust would also provide a good C:N mix but the texture of sawdust is too fine to allow for effective air flow.
It’s important to avoid using certain materials such as coal ash and especially wood chips from pressure-treated lumber. And it’s a good idea to go easy using manure from pets or large quantities of fats, oils or waxes. These types of materials may be difficult to compost or may result in compost containing chemicals that can harm crops or humans. There are too many different combinations of materials to give blanket recommendations about how much of each to mix to get the moisture content and the C:N ratio into reasonable ranges for a good start on the process. One example is given in the box “A Sample Recipe for Backyard Composting.” There are formulas to help you estimate the proportions of the specific materials you might want to use in the compost pile (see Cornell University’s http://compost.css.cornell.edu). Sometimes it will work out that the pile may be too wet, too low in C:N (that means too high in nitrogen), or too high in C:N (too low in nitrogen). To balance your pile, you may need to add other materials or change the ratios used. Adding dry sawdust or wood chips will remedy the first two problems, and adding nitrogen fertilizer will remedy the third. If a pile is too dry, you can add water with a hose or sprinkler system.

One thing to keep in mind is that not all carbon is equally available for microorganisms. Lignin is not easily decomposed. (We mentioned this when discussing soil organisms in Chapter 4 and again in Chapter 9 when we talked about the different effects that various residues have when applied to soil.) Although some lignin is decomposed during composting, probably depending on factors such as the type of lignin and the moisture content, high amounts of carbon present as lignin may indicate that not all of the carbon will be available for rapid composting. This means that the effective C:N can be quite a bit lower than expected based on total carbon (Table 13.1). For some materials, there is little difference between the C:N calculated with total carbon and calculated with only biodegradable carbon.
Pile Location and Size
Composting sites should be appropriately situated. They need to be readily accessible by equipment and because they will have some natural leakage (especially in humid climates), they need to be kept away from watercourses, sinkholes, flood plains, seasonal seeps, wells and other poorly drained areas. Also, depending on the feedstock, composting may be associated with undesirable odors, so it is best to be away from residential areas. Backyard composting can be done in piles or vessels and is best done in a safe location away from children and pets.
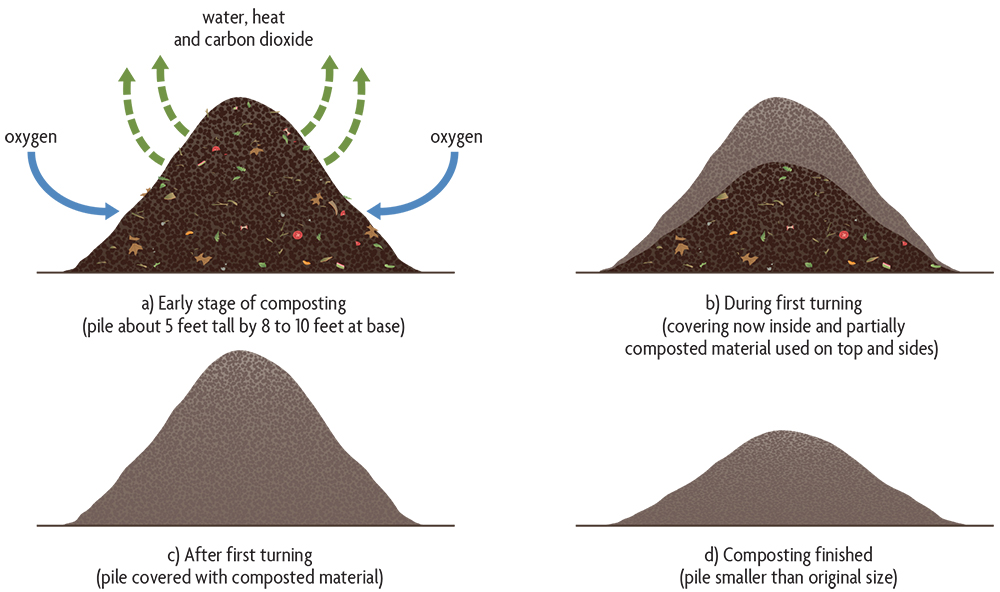
A compost pile or windrow (Figure 13.1) is a large, natural convective structure, something like a set of chimneys next to each other. Oxygen moves into the pile while carbon dioxide, moisture and heat rise out of it. The materials need to fit together in a way that allows oxygen from the air to flow in freely. On the other hand, it is also important that not too much heat escapes from the center of the pile. If small sizes of organic materials are used, a “bulking agent” may be needed to make sure that enough air can enter the pile. Dry leaves, wood shavings/chips and chopped hay or straw are frequently used as bulking agents, which need to be appropriately cut to size to prevent matting and slow composting. Composting will take longer when large particles are used, especially those resistant to decay like large wood chips, while overly fine particles like sawdust decompose well but cause the pile to become too dense for air flow.
COMPOSTING DEAD ANIMALS
The compost pile should be prepared with a base layer of organic absorbent materials, typically 2 inches or less in size with some sizable 4- to 6-inch chunks included. The pile needs to be large enough to retain much of the heat that develops during composting, but not so large and compacted that air can’t easily flow in from the outside. Compost piles should be 3–5 feet tall and about 6–10 feet across the base after the ingredients have settled (see Figure 13.2). (You might want it on the wide side in the winter, to help maintain warm temperatures, while gardeners can make compost in a 3-foot-tall by 3-foot-wide pile in the summer.) Easily condensed material should initially be piled higher than 5 feet. It is possible to have long windrows of composting materials, as long as they are not too tall or wide. —Bonhotal et al. (2008)
Moisture
The amount of moisture in a compost pile is important. If the materials mat and rainwater can’t drain easily through the pile, it may not stay aerobic in a humid climatic zone. On the other hand, if composting is done inside a barn or under dry climatic conditions, the pile may not be moist enough to allow microorganisms to do their job. Moisture is lost during the active phase of composting, so it may be necessary to add water to a pile. In fact, even in a humid region, it is a good idea to moisten the pile at first, if dry materials are used. However, if something like liquid manure is used to provide a high-nitrogen material, sufficient moisture will most likely be present to start the composting process. The ideal moisture content of composting material is about 40–60%, or about as damp as a wrung-out sponge. If the pile is too dry, 35% or less, ammonia is lost as a gas and beneficial organisms don’t repopulate the compost after the temperature moderates. Very dry, dusty composts become populated by molds instead of the beneficial organisms we want.
| Table 13.1 Total Versus Biodegradable Carbon and Estimated C:N Ratios | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Material | % Carbon | C:N | % Carbon | C:N % | Lignin % | Cell Wall % | Nitrogen |
| (Total) | (Biodegradable) | ||||||
| Newsprint | 39 | 115 | 18 | 54 | 21 | 97 | 0.34 |
| Wheat straw | 51 | 88 | 34 | 58 | 23 | 95 | 0.58 |
| Poultry manure | 43 | 10 | 42 | 9 | 2 | 38 | 4.51 |
| Maple wood chips | 50 | 51 | 44 | 45 | 13 | 32 | 0.97 |
| Source: T. Richard (1996a) | |||||||
Monitoring and Turning the Pile
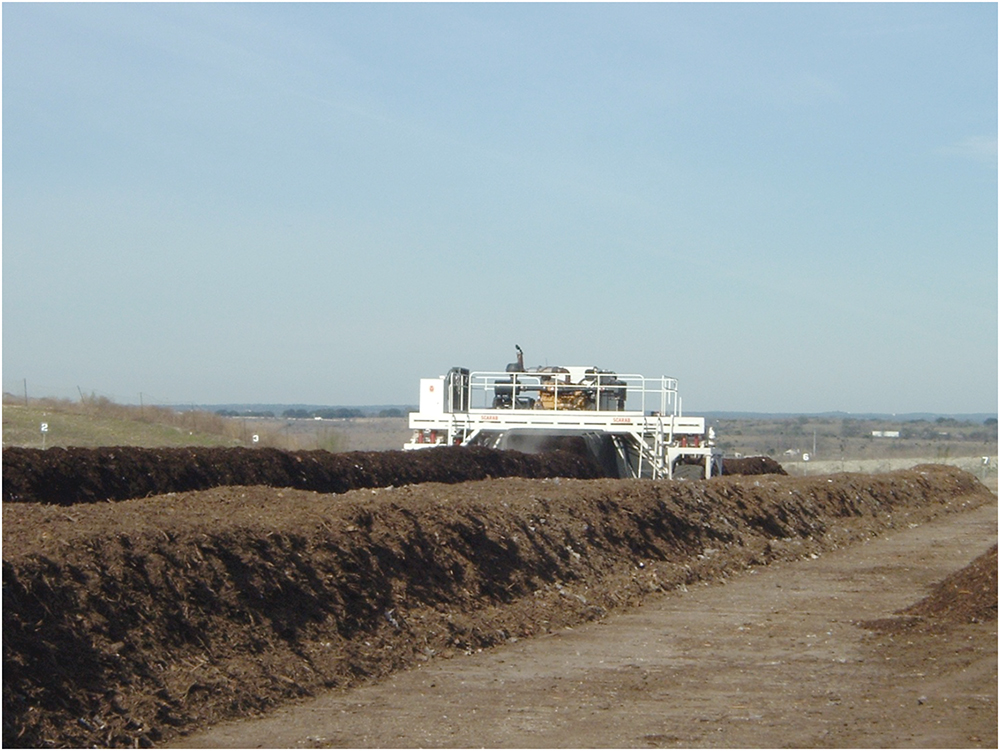
Turning the composting residues exposes all the materials to high-temperature conditions at the center of the pile, and heat convection further exposes upper reaches of the pile (Figure 13.3). Materials at the lower sides of the pile often barely compost. Turning the pile rearranges all the materials and creates a new center. Equipment is now available to quickly turn long compost windrows at large-scale composting facilities (Figure 13.3). Tractor-powered compost turners designed for composting on farms are also available, and some farmers use manure spreaders to build piles. Monitoring of the pile is done primarily by checking temperatures. Internal compost temperatures affect the rate of decomposition as well as the reduction of pathogenic bacteria, fungi and weed seeds. The most efficient temperature range for composting is generally between 104°F and 140°F (40°C and 60°C), however, piles can reach temperatures as high as 170°F (77°C). Spontaneous combustion can be a problem. On the other hand, if temperatures get too high, this can indiscriminately kill beneficial as well as pathogenic organisms, causing temperatures to drop.
Compost temperatures depend on how much of the heat produced by the microorganisms is lost through aeration or surface cooling. During periods of extremely cold weather, piles may need to be larger than usual to minimize surface cooling. As decomposition slows, temperatures will gradually drop and remain within a few degrees of ambient air temperature. Thermometers with long probes and data loggers are available to help monitor the process. Measuring oxygen will also indicate how well the process is progressing. With static piles it is important to keep oxygen levels high by using bulky carbon sources. Ideally, oxygen levels should be kept at 5–14%. If piles are gently turned every time the interior reaches and stabilizes for a few days at about 140°F, it is possible to complete the composting process within months, all other factors of moisture and aeration being optimal. On the other hand, if you turn the pile only occasionally, it may take longer to complete, especially if it has become compacted.
MINIMUM TURNING TECHNIQUE
Farm-quality composts can be produced by turning the pile only once or twice. You need to carefully construct the pile: build it up to reasonable dimensions, use and thoroughly mix materials that give good porosity, and make sure the pile stays moist. A pile that is uniformly heating is getting sufficient air to decompose and therefore may not need turning. As the heat declines, the pile may be getting too dense or not getting sufficient air, and it may need to be turned. A good example of this is composting animal mortalities in wood chips where the pile heats and organic materials degrade without turning.
Although turning compost frequently speeds up the process, too much turning may dry out the pile and cause more nitrogen and organic matter loss. If the pile is too dry, you might consider turning it on a rainy day to help moisten it. If the pile is very wet, you might want to turn it on a sunny day, or cover it with moisture-protective material like chopped straw (like a thatched roof) or compost fleece, a type of breathing cover that is now widely available. Very frequent turning may not be advantageous because it can cause the physical breakdown of important structural materials that aid natural aeration. The right amount of turning depends on a variety of factors, such as aeration, moisture and temperature. Turn your compost pile to avoid cold, wet centers; to break up clumps; and to make the compost more uniform later in the process before use or marketing. Use caution when turning in cold, windy weather if the pile is warm, for it may not reheat.
Finally, piles should not be actively turned in all cases. When composting livestock or roadkill carcasses, the animals are placed in the middle of the pile above a base layer (and lanced to avoid bloating), covered with another 2 feet of organic materials and then allowed to sit for 4–6 months without turning to allow the carcass to fully degrade (see case study at end of chapter).
Controlling Pathogens
Pathogens are a large concern with composts, especially when they involve excrements and carcasses. Different methods of composting will result in varying levels of pathogen reduction. Turned piles will continue to move material into the center of the pile so that all material is exposed to thermophilic temperatures. Different regulators have different time-temperature requirements to meet certain needs. For example, the United States Environmental Protection Agency lists processes to further reduce pathogens, which requires temperature between 131°F and 170°F. To comply with the standard, composting operations that utilize an in-vessel or static aerated pile system must maintain a temperature within that range for a minimum of three days. Composting operations that utilize a windrow composting system must maintain a temperature within that range for a minimum of 15 days, during which time the materials must be turned five times. This protocol is set up to ensure that pathogen levels are low at the time of compost application. It may take longer to kill pathogens in passively aerated windrows than in-vessel or turned piles. Composts from feedstocks with potentially dangerous pathogens will be safer than the original source materials, but caution should still be exercised. It should not be topdressed onto crops that are directly used for human consumption, and composters and applicators need to take precautions for their own health, like wearing masks and protective clothing.
The Curing Stage
Following high-temperature composting, the pile should be left to cure for about one to three months. Usually, this is done once pile temperatures cool to 105°F and high temperatures don’t recur following turning. Curing is especially needed if the active (hot) process is short or poorly managed. There is a reduced need to turn the pile during curing because the phase of maximum decomposition is over and there is significantly less need for rapid oxygen entry into the pile’s center when the decomposition rate is slow. However, the pile may still need turning during the curing stage if it is very large or didn’t really finish composting. Determining when compost is finished is sometimes difficult, but if it reheats, it is not finished. (The Solvita® test measures carbon dioxide losses from compost as a way to determine compost maturity.) Curing the pile furthers aerobic decomposition of resistant chemicals and larger particles. Common beneficial soil organisms populate the pile during curing, the pH becomes closer to neutral, ammonium is converted to nitrate, and soluble salts are leached out if the pile is outside and sufficient precipitation occurs. Be sure to maintain water content at the moisture-holding capacity (around 50% or less during curing) to ensure that active populations of beneficial organisms develop. It is thought that the processes that occur during the early curing stage give compost some of its disease-suppressing qualities. On the other hand, beneficial organisms require sources of food to sustain them. Thus, if composts are allowed to cure for too long, which can deplete all the available food sources, disease suppression qualities may decrease and eventually be lost.
Other Composting Techniques
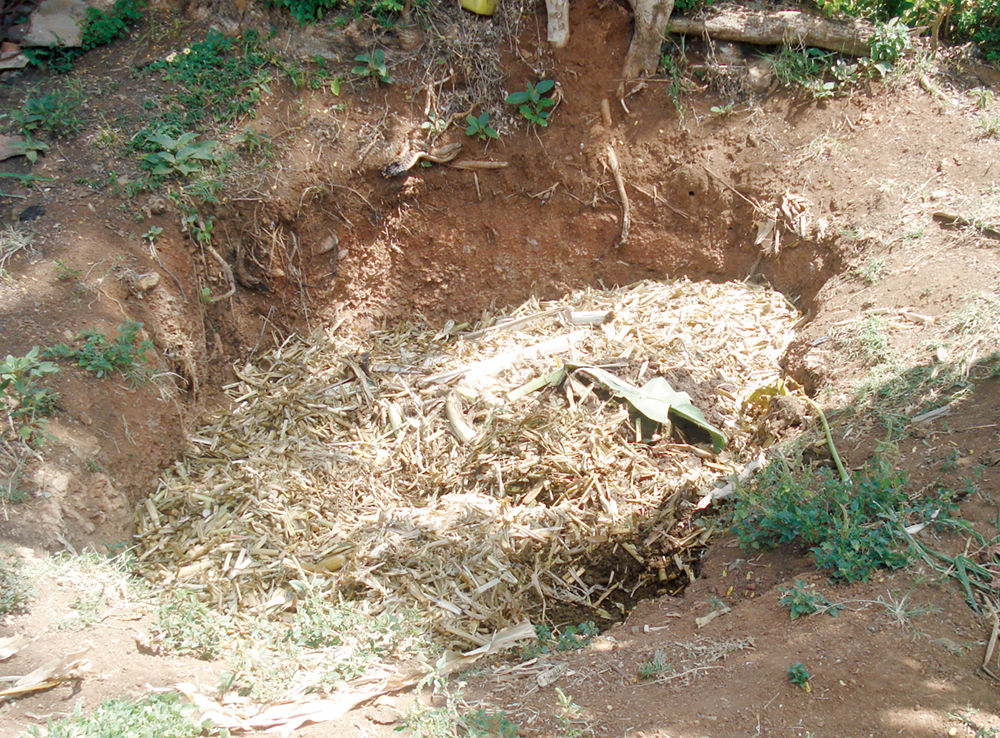
High-temperature (thermophilic) piles or windrows account for most composting, but other methods are also used. Instead of making piles, small farmers in developing countries often dig pits for composting (Figure 13.4), especially in dry and hot climates. The pits can be covered with soil material to prevent animals from getting into them, and they retain moisture in the compost material better. Many home composters prefer using vessels to facilitate the turning process, to have better control over temperature and moisture conditions, and to keep out rodents. But these systems are generally not economical for large-scale commercial operations.
Vermicomposting involves the use of earthworms—typically red worms—to perform the decomposition process. The method is, in a way, still mostly bacteria based, but the process occurs in the gut of the worm. The end product is worm casts, coated with mucus consisting of polysaccharides that make them into somewhat stable aggregates. The system requires bedding materials like newspaper strips, cardboard, hay and similar carbonaceous materials that mimic the decaying dried leaves that worms find in their natural habitat. The process is fast and efficient: worms can process half their weight in organic material in one day. The final product has an attractive feel and smell, and is appealing to consumers.
Vermicomposting is most often used to process kitchen scraps and can be done indoors in small bins. Vermicomposting methods are also used in large commercial operations. Two main approaches are used: windrows or raised beds. With windrows, new materials are added on one side of the bed, and the other side is harvested for compost after about 60 days. With the raised-bed or container system, which is preferred for indoor operations in colder climates, the worms are fed at the top of the beds and the castings are removed at the bottom. Some vermicomposting operations are connected with livestock farms to process manure for export of excess nutrients off the farm as a value-added product.
Fermenting composting, or bokashi, is an anaerobic composting methodology developed in Korea and Japan. The organic feedstock is inoculated with Lactobacilli bacteria that generate a fermentation process under anaerobic conditions, converting a fraction of the carbohydrates to lactic acid. The process is similar to the making of silage and fermented foods (like kimchi and sauerkraut). It is mostly done on a small scale, with food scraps as the primary source material and using a sealed container, but some large-scale bokashi is done with tightly covered windrows. The preserve can be soil applied after a few weeks of fermentation or stored for later use. The process also releases some of the feedstock’s water content, which is high in nutrients. The advantages of the bokashi process are that it is fast and that it produces less odor and fewer greenhouse gas emissions. Disadvantages are the need for sealed containers and ways to capture the liquid discharge, the purchase of fermentation bacteria, and the need to bury the compost into the soil (i.e., not use as topdressing).
Using Composts
Composts help reduce organic waste and are universally beneficial to the soil if applied at appropriate rates and managed well. They can be used on turf, in flower gardens, on trees, and for vegetable and agronomic crops. Composts can be spread and left on the surface or incorporated into the soil by plowing or rototilling. Composts also are used to grow greenhouse crops, and they form the basis of some potting soil mixes. Composts should not be applied annually at high rates. That is a recipe for overloading the soil with nutrients (see discussion in Chapter 7).
Composts benefit the soil by providing nutrients, enhancing biological processes and improving the physical structure. Organic farmers are especially keen on using composts as a way to replenish the nutrients that were extracted by their crops (as they cannot use synthetic fertilizers). Although they can “grow” their own nitrogen with legume rotations and cover crops, most other nutrients need to be restocked with organic materials from external sources. Good compost is ideal because it contains the nutrients and carbon that keep the soil healthy, and compost often suppresses pathogens. Conventional farmers, especially for high-value crops, also like to apply compost as a soil amelioration method to enhance crop yields and to reduce pest pressures and environmental impacts (e.g., by improving water infiltration). Composts are also extensively used in landscaping and gardening as urban soils are often compromised by construction activities and heavy traffic (see Chapter 22 on urban environments). You don’t see a lot of compost use on crops growing on large acreage where the cost is generally too high to justify applications (animal manure application is more common). A recent trend in highway departments is to compost roadkill and apply the product to enhance roadside plantings.
I don’t make compost because it makes me feel good. I do it because composting is the only thing I’ve seen in farming that costs less, saves time, produces higher yields and saves me money.
—Cam Tabb, West Virginia beef and crop farmer
Finished composts provide relatively low amounts of readily available nutrients. During composting, much of the nitrogen is converted into more stable organic forms, although potassium and phosphorus availability remain unchanged. However, it should be kept in mind that composts can vary significantly, and some that have matured well may have high levels of nitrate. Even though most composts don’t supply a large amount of available nitrogen per ton, they still supply fair amounts of other nutrients in available forms and greatly help the fertility of soil by increasing organic matter and by slowly releasing nutrients. Compost materials can be tested at selected commercial agricultural and environmental laboratories, which is especially important if certification is sought.
In some cases, the repeated use of compost, especially on some organic farms, may result in buildup of certain nutrients. For example, if high amounts of compost are applied to meet a crop’s nitrogen needs (remember, compost is relatively low in available nitrogen), then nutrients like phosphorus and potassium are applied in excessive amounts and can accumulate in the soil. Also, salts may build up if there is not enough rainfall to wash them out of the soil (like under high tunnels and in greenhouses). It is recommended to monitor the soil through regular soil tests and to change the fertility strategy accordingly (for example, by using a legume cover crop as a nitrogen source and reducing compost applications).
DISEASE SUPPRESSION BY COMPOSTS
Research by Harry Hoitink and coworkers at Ohio State University shows that composts can suppress root and leaf diseases of plants. This suppression comes about because the plants are generally healthier (microorganisms produce plant hormones as well as chelates that make micronutrients more available) and are therefore better able to resist infection. Beneficial organisms compete with disease organisms for nutrients and either directly consume the disease-causing organisms or produce antibiotics that kill bacteria. Some organisms, such as springtails and mites, “actually search out pathogen propagules in soils and devour them,” according to Hoitink. In addition, Hoitink found that potting mixes containing composts “rich in biodegradable organic matter support microorganisms that induce systemic resistance in plants. These plants have elevated levels of biochemical activity relative to disease control and are better prepared to defend themselves against diseases.” This includes resistance to both root and leaf diseases.
Composts rich in available nitrogen may actually stimulate certain diseases, as was found for phytophthora root rot on soybeans, as well as for fusarium wilts and fire blight on other crops. Applying these composts many months before cropping, allowing the salts to leach away, or blending them with low-nitrogen composts prior to application, reduces the risk of stimulating diseases.
Composting can change certain organic materials used as surface mulches, such as bark mulches, from stimulating disease to suppressing disease.
PROTECTING DRINKING WATER SUPPLIES
Composting of manure is of special interest in watersheds that supply drinking water to cities, such as those that serve New York City. The parasites Giardia lamblia (beaver fever) and Cryptosporidium parvum cause illness in humans and are shed through animal manure, especially young stock. These organisms are very resistant in the environment and are not killed by chlorination. Composting of manure, however, is an economical option that kills the pathogen and protects drinking water.
Advantages of Composting
Composted material is less bulky than the original feedstock, making it less costly to transport. It is also easier and more pleasant to handle. During the composting process, carbon dioxide and water are lost to the atmosphere and the size of the pile decreases by 30–60%. In addition, many weed seeds and disease-causing organisms may be killed by the high temperatures in the pile. Unpleasant odors are also eliminated. Flies, a common problem around manures and other organic wastes, are much less of a problem with composts. Composting reduces or eliminates the decline in nitrogen availability that commonly occurs when organic materials, such as sawdust or straw, are added directly to soil. Compost application can also lower the incidence of plant root and leaf diseases, as mentioned. Moreover, the chelates and the direct hormone-like chemicals present in compost often further stimulate the growth of healthy plants. Then there are the positive effects on soil physical properties that are derived from improving soil organic matter (figures 13.5 and 13.6).
The composting process also helps us address the concerns around nutrient flows we discussed in Chapter 7. When crops are sold off the farm, and sometimes transported over long distances, we remove carbon and nutrients from the fields that in many cases don’t get recycled for economic reasons. Composting allows us to use carbon and nutrients from waste materials and apply them to the soil in a safe and cost-effective manner, thereby reducing the nutrient loss and excess issues that are now inherent in our agricultural system. Sure, we aren’t able to recycle carbon and nutrients in corn or soybeans from an Iowa farm that ended up as manure from California beef or Chinese pigs—the logistics would be inhibitive. But composting that manure makes it easier and more economical to move off a farm with excess nutrients and to help improve nearby fields, gardens and landscapes with local organic resources that would otherwise mostly be a nuisance.
If you have a large amount of organic waste but not much land, composting may be very helpful and may create a valuable commercial product that improves farm profitability. Also, since making compost decreases the solubility of nutrients, composting may help lessen pollution in streams, lakes and groundwater. On many poultry farms and on beef feedlots, where high animal populations on limited land may make manure application a potential environmental problem, composting may be the best method for handling the wastes and removing the excess nutrients. Composted material, with about half the bulk and weight of manure, and a higher commercial value, can be economically transported over significant distances to locations where nutrients are needed. In addition, the high temperatures and biological activity during the composting process can help to decrease antibiotic levels in manures, which can be taken up by crops growing on manured land. Compost can also be stored more easily than the bulk feedstocks, so it can be applied when soil and weather conditions are optimal.
Without denying the good reasons to compost, there are frequently very good reasons to just add organic materials directly to the soil without composting. Compared with fresh residues, composts may not stimulate as much production of the sticky gums that help hold aggregates together. Also, some uncomposted materials have more nutrients readily available to feed plants than do composts. Plants may need readily available nutrients from residues if your soil is very deficient in fertility. Routine use of compost as a nitrogen source may cause high soil phosphorus levels to develop because of the relatively low N:P ratio. Finally, more labor and energy usually are needed to compost residues than when simply applying the uncomposted residues directly. In general, composting makes most sense when 1) the feedstock materials are difficult to handle, unsafe in the open environment, or have odor concerns (like livestock carcasses, or food processing waste), 2) the waste material cannot be used locally and needs to be transported over distances before field application (like urban tree leaves), 3) there are concerns with pathogens (like pet, zoo or human waste) or 4) there is a good market for the use of compost (like farms near urban areas).
Chapter 13 Summary
Composting helps us use organic waste materials to benefit the soil and increase plant growth. It helps reduce problems with local excesses and deficiencies of carbon and nutrients by making them safe and transportable. Composting organic residues before applying them to soil is a tried and true practice that can, if done correctly, eliminate plant disease organisms, weed seeds and many (but not all) potentially noxious or undesirable chemicals. Compost provides extra waterholding capacity to a soil, provides a slow release of N and may help to suppress a number of plant disease organisms as well as enhance the plant’s ability to fight off diseases. Critical to good composting is to have 1) a good balance of carbon (brown-dry) and nitrogen (green or colorful-wet), 2) good aeration, 3) moist conditions and 4) a mass of 4–5 cubic feet to reach and maintain high temperatures. It is also best to turn the pile or windrow to ensure that all the organic materials have been exposed to the high temperatures.


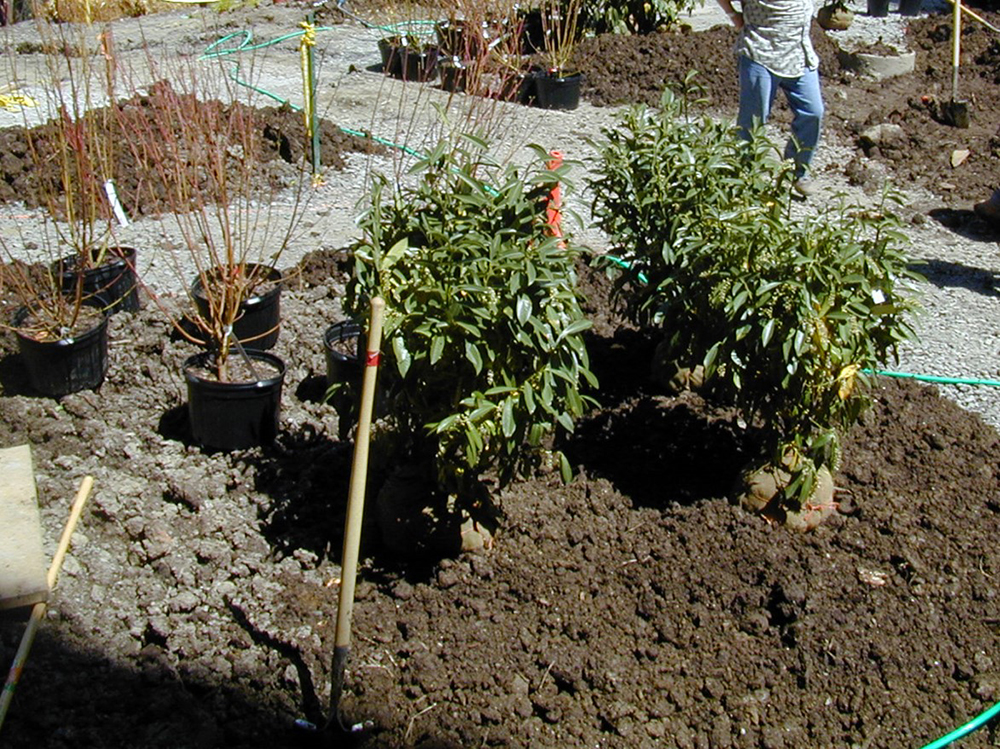
Figure 13.6. Three years of tree growth without (left) and with (right) compost application. Photos by Urban Horticulture Institute, Cornell University.
A Case Study, Cam Tabb
Kearneysville, West Virginia
During droughts in 2006, 2007 and 2010, West Virginia beef farmer Cam Tabb’s crop yields exceeded the averages for his area. At times, neighbors have wondered whether Tabb enjoys some kind of miraculous microclimate, since he seems to make it through dry periods with seemingly little impact.
“I get blamed for getting more water than they got because the corn looks better,” laughs Tabb, who raises 500 Angus beef cattle and grows small grains, hay and corn for grain and silage, using no-till methods, on 1,900 acres near Charles Town, West Virginia. Tabb credits his strong yields to a commitment to no-till practices, which he’s been implementing since the early 1970s, as well as to three decades of applying composted horse, dairy and cattle manure to his fields. “I get a healthier plant with a better root system because my soil structure is better,” he says. “So the rain that you do get really sinks in.”
Tabb’s composting efforts, combined with annual soil tests and rotations, have done more than improve his soil and crop yields; in fact, composting has become one of the farm’s most important sources of income.
Tabb has come a long way since he piled manure on hard-packed ground and watched it ice over in the winter. “Before, I handled the manure as a waste, not a resource,” he says. “I thought it had to smell bad to be any good. That was before I realized that I was smelling nitrogen being lost into the air as ammonia."
Inspired by a West Virginia University researcher’s presentation on backyard composting, Tabb realized he needed to add a carbon source to his manure and to turn the piles to encourage aeration. Once he began mixing in sawdust from horse stalls and turning the piles, he was on his way to becoming a master composter. Now, after years of fine-tuning his operation, he can talk about compost for hours.
He earns money taking in and hauling away a wide range of compostable materials from a faithful clientele—including several municipalities, area fish hatcheries, horse operators and neighbors—that has developed simply through word of mouth. These materials include animal manure, animal carcasses, stumps, storm debris, scrap lumber, pallets, food waste, leaves and grass clippings. “People can pay me at half the cost it would take them to get their trash hauled away,” he says. “We then process and sell the materials we take away.”
The ingenuity of Tabb’s composting operation lies in having found ways to make money several times off of these “waste” materials. For example, he chips scrap wood that he’s been paid to haul from home construction sites and sells that material as bedding to horse operators. He rents containers to the horse owners to store used bedding, containing manure, which he hauls back to his farm, composts and sifts to create a high-grade compost product that he either sells or uses on his farm. He estimates that he composts at least 26,000 cubic yards of horse manure annually.
The fish wastes that Tabb receives from a federal fish hatching facility are composted with sawdust and horse manure. “This quickly creates a nice compost that contains 15–16 pounds N per ton, almost double the N content of our basic compost product,” he says.
Tabb also rents out containers to contractors clearing land of trees and stumps. “When we get logs, we save them aside; they’re better for [reselling as] firewood,” he says. After the soil and rocks are removed from the scraps and split stumps, the wood is mulched and sold to nurseries. The stump dirt, which he describes as being “about 85% dirt and 15% compost” is sifted and screened, creating a topsoil product that he markets back to the contractors for landscaping purposes. “None of the topsoil we sell comes from our own farm,” he says. “It is all from recycled materials that we have brought in.” The topsoil that once was a byproduct of the stump removal service is now one of the top-grossing products he sells, now that he has the equipment to sift the rocks and foreign material out of it.
While “crop response and the reduction of manure volume” are what initially got Tabb excited about composting, today he is particularly motivated by the major role that composting plays in ensuring his farm’s economic sustainability. He says it has paid to have a good compost supply on the farm, and in addition to longer-term benefits of increased organic matter and plant health, it’s more cost efficient than traditional fertilizer.
The water-retention and slow-nutrient-release qualities of his compost have boosted Tabb’s yields in good growing years and have buffered his operation during hard ones. One year, he recorded an 80-bushel corn yield advantage on an acre amended with his compost compared to an acre where no compost had been applied.
Tabb spreads 10–12 tons of compost per acre to his crop fields, depending on soil test results, just once every three years. His compost—which supplies 9, 12 and 15 pounds of nitrogen, phosphorus and potash per ton, respectively—provides, with the exception of nitrogen, sufficient nutrients for his grain and hay crops. The compost he spreads is never less than a year old. Over time, he has become more selective about where he spreads, focusing on fields with 2%–3% organic matter content instead of those that have attained 5%–7%.
Tabb’s windrow piles of compost—“They’re bigger than anything you’ve ever seen,” he says—measure 100 feet long, 20–25 feet wide and 15 feet high. The piles are set up at eight different locations on his farm, which reduces the number of tractor trips, cost and risk of soil compaction while spreading. Since the materials that are used for compost come to the farm by way of truck, he aggregates them adjacent to the acreage where he is going to eventually use the compost.
He relies on experience and observation instead of adhering to strict rules while making compost. “Everyone around the farm knows what to look for in turning the piles,” he says. Heat-loving fungi, stimulated into releasing spores once the pile heats up to temperatures above 140°F, form mushrooms as the pile cools down. “We wait until the temperature goes under 130°F and turn the pile when we see the fragile mushrooms,” he explains. He adds, “We never turn a pile that is going upwards in heat,” so that piles will reach sufficient temperatures to kill pathogens and weed seeds. Turning, which Tabb does with a front-end loader, pays for itself by reducing the volume of the pile. Turning also stimulates more rapid and thorough decomposition of materials in the pile, inducing temperatures hot enough to kill weed seeds and diseases. Based on his experience, Tabb recommends maintaining a large ratio of old to fresh materials within compost piles. This ensures that the moisture released from fresh materials will be absorbed by drier, older materials, thus preventing leachate formation and speeding the piles’ overall inoculation and decomposition rates.
Tabb is pleased by the long-term results of applying compost at his farm in conjunction with no-till, where the soil has taken on a spongier feel and has become more abundant in earthworms. He also sees little to no runoff from his compost-treated fields. “Our land makes up a total small watershed, and our springs feed a federal fish hatchery. If there were any negative runoff in the water, it’d be ours, and we’d hear about it from the people downstream,” he observes.
Impressed by his results, several of Tabb’s neighbors now make and spread their own “black gold.” says Tabb, “Almost any farmer would understand what I do. I hadn’t realized that I was a practicing environmentalist, but almost every farmer is. These days, you can’t afford not to be.”
Chapter 13 Sources
Aldrich, B. and J. Bonhotal. 2006. Aerobic composting affects manure’s nutrient content. Northeast Dairy Business 8(3):18.
Bonhotal, J., E. Stahr and M. Schwartz. 2008. A how-to on livestock composting. Northeast Dairy Business 10(11): 18–19.
Brown, N. 2012. Worker protection at composting sites. Biocycle 53(1):47.
Cornell Waste Management Institute. 2020. http://cwmi.css.cornell.edu/.
Epstein, E. 1997. The Science of Composting. Tech-nomic Publishing Company: Lancaster, PA.
Hoitink, H.A.J., D.Y. Han, A.G. Stone, M.S. Krause, W. Zhang and W.A. Dick. 1997. Natural suppression. American Nurseryman (October 1): 90–97.
Martin, D.L. and G. Gershuny, eds. 1992. The Rodale Book of Composting: Easy Methods for Every Gardener. Rodale Press: Emmaus, PA.
Millner, P.D., C.E. Ringer and J.L. Maas. 2004. Suppression of strawberry root disease with animal manure composts. Compost Science and Utilization 12: 298–307.
Natural Rendering: Composting Livestock Mortality and Butcher Waste. Cornell Waste Management Institute. http://compost.css.cornell.edu/naturalrenderingFS.pdf.
Richard, T. 1996a. The effect of lignin on biodegradability. http://compost.css.cornell.edu/calc/lignin.html.
Richard, T. 1996b. Solving the moisture and carbon-nitrogen equations simultaneously. http://compost.css.cornell.edu/calc/ simultaneous.html.
Rothenberger, R.R. and P.L. Sell. Undated. Making and Using Compost. Extension Leaflet (File: Hort 72/76/20M). University of Missouri: Columbia, MO.
Rynk, R., ed. 1992. On Farm Composting. NRAES-54. Northeast Regional Agricultural Engineering Service: Ithaca, NY.
Staff of Compost Science. 1981. Composting: Theory and Practice for City, Industry, and Farm. JG Press: Emmaus, PA.
Seymour, R.S. 1991. The brush turkey. Scientific American (December).
Weil, R.R., D.B. Friedman, J.B. Gruver, K.R. Islam and M.A. Stine. Soil Quality Research at Maryland: An Integrated Approach to Assessment and Management. Paper presented at the 1998 ASA/CSSA/SSSA meetings, Baltimore. This is the source of the quote from Cam Tabb.






